Backache Disease
One of the most frequent reasons people leave work or seek medical attention is Backache Disease. One of the main causes of disability in the globe is back pain. Thankfully, there are ways to avoid or lessen the majority of back pain episodes, particularly in those under 60. If prevention doesn’t work, the back can usually be healed in a few weeks with basic home remedies and proper body usage. Back pain is rarely treated with surgery.
Signs and Symptoms Backache Disease
From a muscle soreness to a scorching, stabbing, or shooting sensation, back pain can take many forms. Additionally, a leg may experience radiating pain. Pain can worsen when you bend, twist, raise, stand, or walk.
When to consult a doctor??
With self-care and at-home therapy, most back pain gets better over time, frequently in a matter of weeks. For back discomfort, speak with your healthcare provider about:
– Endures for more than a few weeks.
– Is terrible and does not get better when you sleep.
– Spreads, particularly if it reaches below the knee, down one or both legs.
– Causes one or both legs to become weak, numb, or tingly.
– Accompanied with inexplicable weight reduction.
Back discomfort in certain individuals may indicate a major health issue. Although it is uncommon, get help right away if you have back discomfort that:
– Causes fresh issues with the bladder or bowel.
– Is coupled with a fever.
– After being hit in the back, falling, or suffering another injury.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Back
• Four regions of the spine: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacrum and coccyx.
• Key structures include vertebrae, spinal cord, intervertebral discs, ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
• Vertebrae: Small bones protecting the spinal cord.
• Spinal cord: Long bundle of nerves running down the back.
• Intervertebral discs: Cushion-like pads between vertebrae.
• Ligaments: Short bands of tough, flexible tissue holding vertebrae in place.
• Tendons: Cord connecting muscle to bone.
Risk Factors of Backache Disease
1. Fitness Level: Back pain is more common in those not physically fit, especially those with weak back and stomach muscles. Over-exercising after inactivity increases the risk.
2. Weight Gain: Obesity and an inactive lifestyle can lead to weight gain, putting stress on the back.
3. Job-Related Risk Factors: Heavy lifting, pushing, pulling, or twisting jobs can injure the back. Poor posture and uncomfortable chair positions can also contribute.
4. Stress Level: Chronic poor sleep, depression, or anxiety can increase the frequency and severity of back pain.
5. Age: Back pain becomes more common with age, especially after 45.
6. Hereditary Factors: Genetics can influence some back pain disorders.
3 Tips of Thread Face Lift
Types of Back Diseases
The following are some ways that medical professionals and researchers define the many forms of back pain:
- Acute back pain typically lasts a few days to a few weeks and occurs suddenly.
- Subacute back pain lasts four to twelve weeks and might develop gradually or all at once.
- Chronic back pain can develop gradually or rapidly, persist for more than 12 weeks, and be experienced every day.
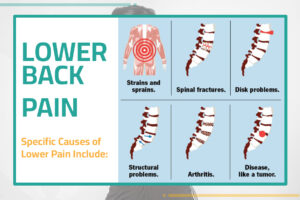
Common Causes of Back Illness
- Muscle or ligament strain: Repeated heavy lifting or awkward movements can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments, leading to painful muscle spasms.
• Bulging or ruptured disks: Disks act as cushions between spine bones, but may not cause back pain.
• Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back, leading to spinal stenosis.
• Osteoporosis: Porous and brittle bones can cause painful breaks in the spine’s vertebrae.
• Ankylosing spondylitis: This inflammatory disease can fuse some spine bones, making the spine less flexible.
Structural Problems Cause Back Pain
• Ruptured disks: Increased pressure on nerves due to ruptured or bulging disks.
• Sciatica: Sharp pain in the buttock and leg due to pressure from bulging or herniated disks or muscle.
• Osteoarthritis: Joint problems in hips, lower back, and other areas. Spinal stenosis, narrowing of space around the spinal cord.
• Unusual spine curvature: Spine scoliosis, a side-curving spine, can cause back pain.
• Osteoporosis: Brittle and porous bones, including spine vertebrae, increase risk of compression fractures.
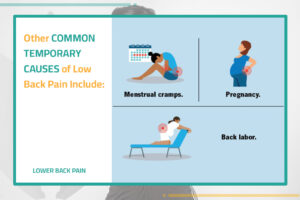
• Kidney problems: Kidney stones or kidney infections can cause back pain.
How to Do a Full- Body Stretching Routine?
Infections
An infection in the area between your vertebra and the outermost layer of meninges (dura mater) is known as a spinal epidural abscess. In addition to back discomfort, you can experience other symptoms like fever, trouble voiding, or lack of control over urinating and/or defecating.
An infection of the bones in your spine is called vertebral osteomyelitis. Usually, it results in lower back pain that doesn’t go away when you’re sleeping. In addition to other symptoms like a fever, the afflicted bone or bones may feel sensitive to the touch.
Home Treatments for Back Pain
Traditional back pain treatments can be combined with a variety of home remedies. Consult your physician if you have any queries about these.
Ice and heat therapy for backache disease
In the short-term stages of back pain, ice packs may help reduce inflammation and ease discomfort. Please take care not to put the ice straight on your skin. To protect your skin, wrap it in gauze or a thin towel. Once inflammation has decreased, warm compresses may also help with pain relief. Think about alternating between cold and heat.
Workouts
One therapy option that should be seriously explored is exercise to strengthen the core muscles, which are the muscles in the back and abdomen, and to improve posture.
This therapy frequently entails:
– Utilizing appropriate lifting techniques to improve posture
– Enhancing the strength of the core muscles
– To increase flexibility, stretch your muscles.
– You can learn how to do these kinds of exercises at home from a physical therapist.